Two coaxial solenoids of different radii carry current \(I\) in the same direction. Let \(\vec{F}_1\) be the magnetic force on the inner solenoid due to the outer one and \(\vec{F}_2\) be the magnetic force on the outer solenoid due to the inner one. Then:
| 1. | \(\overrightarrow{{F}_1}=\overrightarrow{F_2}=0\) |
| 2. | \(\vec{F}_1\) is radially inwards and \(\vec{F}_2\) is radially outwards |
| 3. | \(\vec{F}_1\) is radially inwards and \(\vec{F}_2=0\) |
| 4. | \(\vec{F}_1\) is radially outwards and \(\vec{F}_2=0\) |
Two long current carrying thin wires, both with current \(I\), are held by insulating threads of length \(L\) and are in equilibrium as shown in the figure, with threads making an angle '\(\theta\)' with the vertical. The mass per unit length of wires is \(\lambda\), then the value of \(I\) is:
(\(g=\) gravitational acceleration)
1. \( \sin \theta \sqrt{\frac{\pi \lambda g L}{\mu_0 \cos \theta}} \)
2. \( 2 \sin \theta \sqrt{\frac{\pi \lambda g L}{\mu_0 \cos \theta}} \)
3. \( 2 \sqrt{\frac{\pi g L}{\mu_0} \tan \theta} \)
4. \( 2 \sqrt{\frac{\pi \lambda g L}{\mu_0} \tan \theta}\)
| 1. |  |
3. |  |
| 2. |  |
4. |  |
A rigid square loop of side \(a,\) carrying a current \(I_2,\) lies on a horizontal surface near a long, straight wire carrying a current \(I_1.\) Both the loop and the wire are in the same plane, as shown in the figure. The net force acting on the loop due to the current in the wire is:
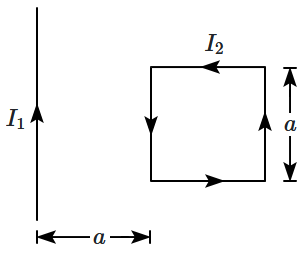
| 1. | zero |
| 2. | repulsive and equal to \( \dfrac{\mu_0 I_1 I_2}{4 \pi} \) |
| 3. | repulsive and equal to \( \dfrac{\mu_0 I_1 I_2}{2 \pi} \) |
| 4. | attractive and equal to \(\dfrac{\mu_0 I_1 I_2}{3 \pi}\) |
Two wires \(A\) & \(B\) are carrying currents \(I_1\) & \(I_2\) as shown in the figure. The separation between them is \(d\). A third wire \(C\) carrying a current \(I\) is to be kept parallel to them at a distance \(x\) from \(A\) such that the net force acting on it is zero. The possible values of \(x\) are:
| 1. | \( x=\left(\frac{I_1}{I_1-I_2}\right) d \text { and } x=\frac{I_2}{\left(I_1-I_2\right)} d \) |
| 2. | \( x= \pm \frac{I_1 d}{\left(I_1-I_2\right)} \) |
| 3. | \( x=\left(\frac{I_1}{I_1-I_2}\right) d \text { and } x=\frac{I_2}{\left(I_1-I_2\right)} d \) |
| 4. | \( x=\left(\frac{I_2}{I_1-I_2}\right) d \text { and } x=\frac{I_2}{\left(I_1-I_2\right)} d\) |
1. \(1\)
2. \(2.4\)
3. \(1.4\)
4. \(2\)

| 1. | \(1.2\times 10^{-5}~\text{N}\) directed towards wire \(\mathrm{X}\). |
| 2. | \(1.2\times 10^{-4}~\text{N}\) directed away from wire \(\mathrm{X}\). |
| 3. | \(1.2\times10^{-4}~\text{N}\) directed towards wire \(\mathrm{X}\). |
| 4. | \(2.4\times 10^{-5}~\text{N}\) directed towards wire \(\mathrm{X}\). |
| 1. | \(4\) times | 2. | \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) times |
| 3. | \(8\) times | 4. | \(\dfrac{1}{8}\) times |






